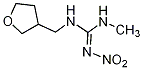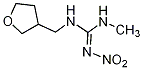
NOMENCLATURE
Common name dinotéfurane ((
m) F-ISO); dinotefuran (BSI, E-ISO)
IUPAC name (
RS)-1-methyl-2-nitro-3-(tetrahydro-3-furylmethyl)guanidine
Chemical Abstracts name N-methyl-
N′-nitro-N′′-[(tetrahydro-3-furanyl)methyl]guanidine
CAS RN [165252–70–0]
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 202.2
M.f. C
7H
14N
4O
3 Form White crystalline solid.
M.p. 107.5 °C
B.p. Decomp. 208 °C
V.p. <1.7 × 10
-3 mPa (30 °C)
Kow logP = –0.549 (25 °C)
Henry 8.7 × 10
-9 Pa m
3 mol
-1 (calc.)
S.g./density 1.40
Solubility In water 39.8 g/l (20 °C). In hexane 9.0 × 10
-6, heptane 11 × 10
-6, xylene 72 × 10
-3, toluene 150 × 10
-3, dichloromethane 61, acetone 58, methanol 57, ethanol 19, ethyl acetate 5.2 (all in g/l, 20 °C).
Stability Stable at 150 °C (
DSC). Hydrolysis
DT50 >1 y (
pH 4, 7, 9). Photodegradation DT
50 3.8 h (sterilised/natural water).
pKa 12.6 (20 °C)
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Agonist of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, affecting the synapses in the insect central nervous system.
Mode of action Systemic insecticide with translaminar activity and with contact and stomach action. Readily taken up by the plant and further distributed acropetally.
Uses Controls a range of sucking insects, such as whiteflies, plant bugs, leafhoppers and mealybugs;
Coleoptera, such as Colorado Beetles and flea Beetles;
Diptera, such as leaf miner flies; and certain
Lepidoptera, such as fruit moths, in vegetables, fruit, paddy rice and turf. Can be applied on foliage, soil, nursery boxes and to paddy water by spray, drench, broadcast and pricking-in-hole treatments.
Formulation types DL;
DP; FL;
GR;
SG;
SL;
WP.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rats, extensively absorbed and completely eliminated within 168 h, mainly via urine. Little metabolism occurred.
Plants In lettuce, metabolites include 1-methyl-3-(tetrahydro-3-furylmethyl)guanidine and 1-methyl-3-(tetrahydro-3-furylmethyl)urea.
Soil/Environment Aqueous photolysis
DT50 1.8 d. Soil DT
50 50–100 d. The major degradate is 1-methyl-2-nitroguanidine.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral
LD50 for male rats 2804, female rats 2000, male mice 2450, female mice 2275 mg/kg.
Skin and eye Acute percutaneous
LD50 for male and female rats >2000 mg/kg. Slight eye and skin irritant (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs).
Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >4.09 mg/l.
NOEL NOAEL (1 y) for male dogs 559, female dogs 22 mg/kg daily.
ADI (
EPA)
aRfD 1.25,
cRfD 0.02 mg/kg [2004]; (
FSC) 0.22 mg/kg
b.w. [2005]
Other Not a mutagen, neurotoxin, carcinogen, teratogen or reproductive toxin.
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral
LD50 for Japanese quail >2000 mg/kg.
LC50 (5 d) for mallard ducks >5000
ppm (997.9 mg/kg daily), Japanese quail >5000 ppm (1301 mg/kg daily).
Fish LC50 (96 h) for carp, rainbow trout and bluegill sunfish >100
ppm.
Daphnia EC50 (48 h) >1000
ppm.
Algae EbC50 (72 h) for
Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata >100 mg/l.
Other aquatic spp. LC50 (48 h) for crayfish 4.84 ppm. LC
50 (96 h) for eastern oysters 141, mysid shrimps 0.79 ppm.
EC50 for
Lemna gibba >110 ppm.
Bees Highly toxic to honeybees;
LD50 (oral) 0.023 μg/bee; (contact) 0.047 μg/bee (
EPA Fact Sheet).
Other beneficial spp. Highly toxic to silkworms.