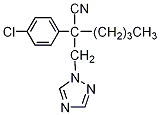
NOMENCLATURE
Common name myclobutanil (BSI, ANSI, E-ISO, (
m) F-ISO)
IUPAC name 2-
p-chlorophenyl-2-(1
H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)hexanenitrile; 2-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(1
H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)hexanenitrile
Chemical Abstracts name α-butyl-α-(4-chlorophenyl)-1
H-1,2,4-triazole-1-propanenitrile
CAS RN [88671–89–0] EC no. 410–400–0
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 288.8
M.f. C
15H
17ClN
4 Form Odourless, white crystalline solid (pure); pale yellow solid (
tech.).
M.p. 70.9 °C (
tech.)
B.p. 390.8 °C/97.6 kPa
V.p. 1.98 × 10
-1 mPa (20 °C)
Kow logP = 2.94 (
pH 7–8, 25 °C)
Henry 4.33 × 10
-4 Pa m
3 mol
-1 (
pH 7, calc.)
Solubility In water 124 (
pH 3), 132 (pH 7), 115 (pH 9–11) (all in mg/l, 20 °C). In acetone, ethyl acetate, methanol, 1,2-dichloroethane >250, xylene 270,
n-heptane 1.02 (all in g/l, 20 °C).
Stability Stable in water (
pH 4–9) at 25 °C. Stable to photolysis.
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibits ergosterol biosynthesis (sterol demethylation inhibitor).
Mode of action Systemic fungicide with protective and curative action. Translocated upwards in the plant.
Uses Control of
Ascomycetes, Fungi Imperfecti and
Basidiomycetes on a wide variety of crops. The primary use is for powdery mildew (
Uncinula necator) control in vines, and for combined leaf scab and powdery mildew control in apples. Application rates vary, typically 30–140 g/ha. Also registered for control of Ascomycetes or Basidiomycetes diseases on a broad variety of crops including other pome fruit, stone fruit, cucurbits, strawberries, almonds, tomatoes, soya beans, vegetables, hops, cotton, cereal seed treatments, turf and ornamentals. It is used as a foliar treatment for control of powdery mildew, shot-hole, blossom blight, anthracnose and rust in stone fruit and nuts; powdery mildew in cucurbits; powdery mildew and rusts on ornamentals; rusts on perennial grasses grown for seed; as a seed treatment for control of seed- and soil-borne diseases in barley, maize, cotton, rice and wheat; and as a post-harvest treatment in crops such as bananas.
Formulation types EC;
EW;
FS;
SC;
WP.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In cows and hens, myclobutanil undergoes metabolism via an oxidative pathway, non-aromatic hydroxylation of the side-chain to form the alcohol, which is further reduced to form the ketone, the carboxylic acid, cyclised to form the lactone, or undergoes conjugation to the sulfate.
Plants In grapes, apples and sugar beet, myclobutanil is metabolised by two routes: i) non-aromatic hydroxylation of the side-chain to form the alcohol, conjugated with sugar and reduced; ii) substitution of the triazole ring, leading to triazolylalanine.
Soil/Environment DT50 (lab., aerobic, 20 °C) 192–574 d (mean 354 d) to give minor metabolites. Under field conditions (Germany, early summer application), biphasic DT
50 9–33 d (mean 23 d); DT
90 >1 y. However, accumulation studies showed that residues do not accumulate following repeated applications. Soil adsorption
Koc 224–920 ml/g (mean 517 ml/g). Stable to both hydrolysis and photolysis, but dissipates rapidly from water to sediment with DT
50 4–20 d (lab., 20 °C) in river and pond water systems. Myclobutanil has a very low vapour pressure and significant amounts will not be present in air; confirmed in a wind tunnel study. Atmospheric DT
50 7.6 h (est., from modelled photochemical oxidative degradation studies).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral
LD50 for male rats 1600, female rats 1800 mg/kg.
Skin and eye Acute percutaneous
LD50 for rabbits >5000 mg/kg. Not a skin irritant; can cause irritation to the eyes (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs).
Inhalation LC50 for rats 5.1 mg/l.
NOEL Dietary
NOEL (90 d) for dogs 56 mg/kg b.w. daily. Reproductive NOEL for rats 16 mg/kg b.w. daily.
NOAEL, based on chronic feeding, oncogenicity and reproductive studies, 2.5 mg/kg b.w.. daily.
ADI (
JMPR) 0.03 mg/kg
b.w. [1992]; (
EC) 0.025 mg/kg b.w.; (
EPA)
cRfD 0.025 mg/kg b.w. [1995].
Other Non-teratogenic in rats and rabbits, and various mutagenicity tests proved negative. Not mutagenic in the Ames assay.
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.)
III.
EC classification R63|
Xn;
R22|
Xi;
R36| N;
R51,
R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral
LD50 for bobwhite quail 510 mg/kg. Dietary
LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5000 mg/kg.
Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 4.4, rainbow trout 2.0 mg/l.
ELS NOEC for fathead minnows 1.0 mg/l.
Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 17 mg/l.
Algae EC50 (96 h) for
Scenedesmus subspicatus 0.91 mg/l.
Other aquatic spp. NOEC for sediment-dwelling organisms (
Chironomus riparius) 5.0 mg/l.
Bees Non-toxic to bees.
LD50 (oral) >171 μg ‘Systhane 20EW’/bee (>33.9 μg active/bee); (contact) 200 μg ‘Systhane 20EW’/bee (>39.6 μg active/bee).
Worms Acute
LC50 for
Eisenia foetida 99 mg/kg; reproduction
NOEC for
Eisenia foetida >10.3 mg/kg.
Other beneficial spp. Harmless in Tier 1 laboratory studies on
Aphidius rhopalosiphi,
Pardosa sp.
, and
Coccinella septempunctata (
IOBC).
