NOMENCLATURE
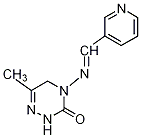
Common name pymétrozine ((
f) F-ISO); pymetrozine (BSI, E-ISO)
IUPAC name (
E)-4,5-dihydro-6-methyl-4-(3-pyridylmethyleneamino)-1,2,4-triazin-3(2
H)-one
Chemical Abstracts name (
E)-4,5-dihydro-6-methyl-4-[(3-pyridinylmethylene)amino]-1,2,4-triazin-3(2
H)-one
CAS RN [123312–89–0]
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is ≥95% pure.
Mol. wt. 217.2
M.f. C
10H
11N
5O
Form Crystalline solid.
M.p. 217 °C
V.p. <4 × 10
-3 mPa (25 °C) (
OECD 104)
Kow logP = –0.18 (
OECD 107)
Henry <3.0 × 10
-6 Pa m
3 mol
-1 (calc.)
S.g./density 1.36 (20 °C)
Solubility In water 0.29 g/l (
pH 6.5, 25 °C). In ethanol 2.4, hexane <0.001, toluene 0.034, dichloromethane 1.2,
n-octanol 0.45, acetone 0.94, ethyl acetate 0.26 (all in g/l, 25 °C).
Stability Stable in air (
OECD 113/
DTA). Hydrolysis
DT50 5–12 d (
pH 5); 616–800 d (pH 7); 510–1212 d (pH 9, 25 °C).
pKa 4.06
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Novel, unidentified biochemistry.
Mode of action Insecticide selective against Homoptera, causing them to stop feeding.
Uses Control of aphids and whitefly in vegetables, potatoes, ornamentals, cotton, deciduous and citrus fruit, tobacco and hops; both juvenile and adult stages are susceptible. Also control of planthoppers in rice. Application rates vary from 150 g/
ha on potatoes to 200–300 g/ha on ornamentals, tobacco and cotton; 10–30 g/hl on vegetables, fruit and hops.
Formulation types DP;
GR;
WG;
WP.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Extensively and rapidly absorbed (
c. 90% in 24 h). Quickly and efficiently eliminated (mainly via excreta) and extensively metabolised in all species tested (rats, farm animals), without accumulation in most major animal food products. Metabolism is via oxidation of the methyl and triazine methylene, and cleavage between the triazine and pyridine rings. The metabolic pathways are similar for all species. Pymetrozine is the relevant residue for assessing the consumer exposure to treated animal food products.
Plants The basic degradation steps are similar in all investigated crops; pymetrozine is the only relevant compound for residue definition.
Soil/Environment In soils, very rapidly and strongly adsorbed;
Kf 3.1–47.7 ml/g,
Koc 246–7875 ml/g
o.c. (10 soils, mean 2245 ml/g o.c.); low mobility and low leaching potential. Soil
DT50 2–69 d (field, 7 soils, median 14 d), DT
90 55–288 d (field, 7 soils, median 185 d). Rapidly degraded in slightly acidic or sunlight-exposed surface water; DT
50 in surface water 5.2–6.6 d (lab., darkness, 2 water-sediment systems). Slightly volatile. In air, efficiently removed by direct photolysis and photochemically induced oxidation.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral
LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg.
Skin and eye Acute percutaneous
LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs,
M&K).
Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >1800 mg/m
3 air.
NOEL (2 y) for rats 3.7 mg/kg b.w. daily; (90 d) for dogs 3 mg/kg b.w. daily; (1 y, oral) for dogs 5.33 mg/kg b.w.. daily.
ADI (
EC) 0.03 mg/kg
b.w.;
aRfD 0.1 mg/kg b.w. [2001]; (
EPA) aRfD 0.01 mg/kg b.w. (females aged 13–49), 0.125 mg/kg b.w. (general population),
cRfD 0.0038 mg/kg b.w. [2005].
Other Non-mutagenic in 5 assay tests.
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.)
III (company classification).
EC classification R40|
R52,
R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral
LD50 for mallard ducks >2000 mg/kg.
LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail >5200
ppm.
Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout, sheepshead minnows and common carp >100 mg/l.
Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 87 mg/l.
Algae LC50 (72 h) for
Scenedesmus subspicatus 47.1 mg/l; (5 d) for
Selenastrum capricornutum 21.7 mg/l.
Other aquatic spp. EC50 (96 h) for eastern oysters 3.05
ppm.
Bees LD50 (48 h) (oral) >117 μg/bee; (contact) >200 μg/bee.
Worms LC50 (14 d) for
Eisenia foetida 1098 mg/kg soil.
Other beneficial spp. Harmless to
Aleochara bilineata,
Poecilus cupreus,
Typhlodromus pyri,
Aphidius matricariae and
Chrysoperla carnea; slightly harmful to
Orius insidiosus; moderately harmful to
Aphidius colemani (
IOBC).
