NOMENCLATURE
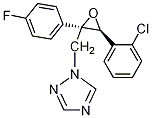
Common name époxiconazole ((
m) F-ISO); epoxiconazole (BSI, E-ISO)
IUPAC name (2
RS,3
SR)-1-[3-(2-chlorophenyl)-2,3-epoxy-2-(4-fluorophenyl)propyl]-1
H-1,2,4-triazole
Chemical Abstracts name cis-1-[[3-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-(4-fluorophenyl)oxiranyl]methyl]-1
H-1,2,4-triazole
CAS RN [133855–98–8], formerly
[106325–08–0] and
[205862–63–1];
[135319–73–2] stereochemistry undefined
EC no. 406–850–2
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Material is the 2
R,3
S- 2
S,3
R- enantiomer pair.
Mol. wt. 329.8
M.f. C
17H
13ClFN
3O
Form Colourless crystals.
M.p. 136.2–137 °C
V.p. <0.01 mPa (20 °C)
Kow logP = 3.33 (
pH 7)
Henry <4.71 × 10
-4 Pa m
3 mol
-1 (calc.)
S.g./density 1.384 (room temperature)
Solubility In water 6.63 × 10
-4 g/100 ml (20 °C). In acetone 14.4, dichloromethane 29.1, heptane 0.04 (all in g/100 ml).
Stability No hydrolysis at
pH 5 and pH 7 within 12 days.
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibition of C-14-demethylase in sterol biosynthesis.
Mode of action Preventive and curative fungicide.
Uses Broad-spectrum Fungicide, with preventive and curative action, for control of diseases caused by
Ascomycetes,
Basidiomycetes and
Deuteromycetes in bananas, cereals, coffee, rice, corn, peanut and sugar beet, generally at 125 g/
ha.
Formulation types EC;
SC;
SE.
Compatibility Compatible with morpholines, MBC-derivatives, azoles, strobilurins and carboxamides.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals A.i. is readily excreted via faeces. There are no major metabolites, but a high number of minor metabolites was identified. The important metabolic reactions were cleavage of the oxirane ring, hydroxylation of the phenyl rings and conjugation.
Plants There is extensive degradation.
Soil/Environment Degradation in soil is by microbial activity,
DT50 c. 2–3 mo.
Koc 957–2647.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral
LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg.
Skin and eye Acute percutaneous
LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to eyes and skin of rabbits.
Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >5.3 mg/l air.
NOEL (carcinogenicity) for mice 0.81 mg/kg b.w.
ADI (
EC) 0.008 mg/kg
b.w. [2008]; (
EPA)
aRfD 0.05,
cRfD 0.02 mg/kg [2006].
EC classification R40|
R62|
R63| N;
R51,
R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral
LD50 for quail >2000 mg/kg.
LC50 for quail 5000 mg/kg.
Fish LC50 (96 h) for trout 2.2–4.6, bluegill sunfish 4.6–6.8 mg/kg.
Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 8.7 mg/l.
Algae EC50 (72 h) for green algae 2.3 mg/l.
Bees LD50 >100 μg/bee.
Worms EC50 (14 d) >1000 mg/kg soil.
